With the implementation of GST, 2017 saw a complete change in the way we used to pay our taxes. Scroll down for more details on how the government of India gets it money and pick the trend you want to see: personal income tax, corporate taxes, service tax, excise or customs duties.
SOURCES OF REVENUE
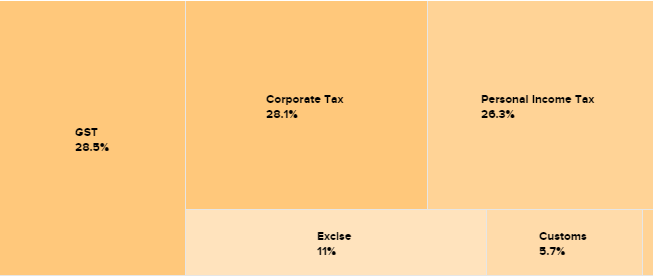
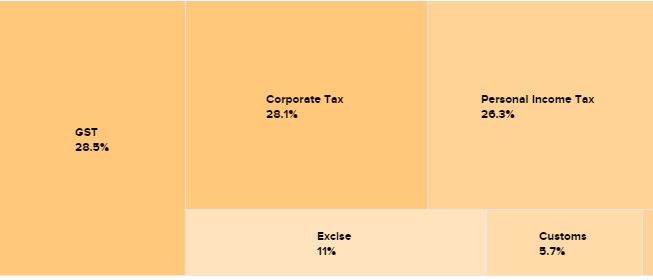
Tax revenue is the government’s income from different kinds of taxes: direct taxes (personal income tax and corporate tax) accounted for 51.3% of total revenues in 2016-17 and the rest came from indirect taxes. Because of the introduction of GST from July 2017, the government’s revenues are undergoing a makeover from this year as all indirect taxes (with the exception of customs duties) are now decided by the GST Council and not the Government of India. Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents.
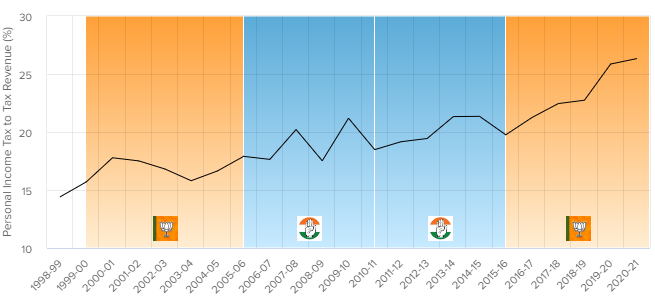
PERSONAL INCOME TAX TREND
This is the proportion of tax revenue that comes from the incomes of Indian citizens. Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents
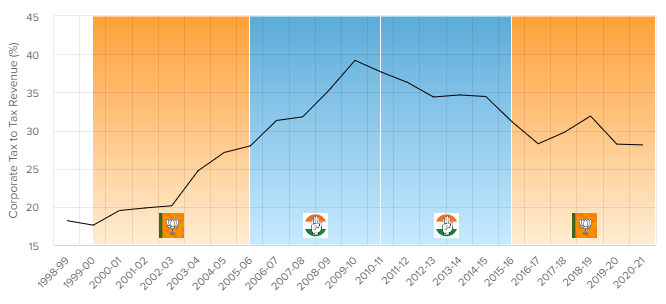
CORPORATE TAX TREND
This is the proportion of tax revenue that comes from company profits.
Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents
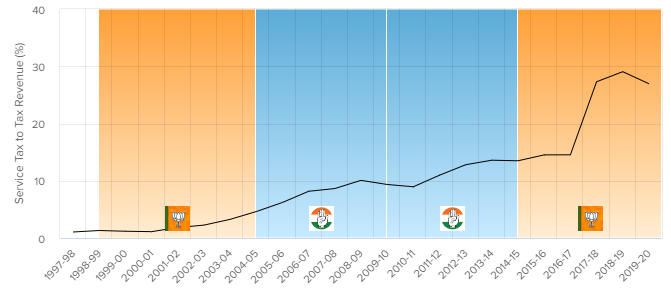
SERVICE TAX TREND
This the contribution to government funds that comes from taxes on services (like say eating out in restaurants, on mobile phone bills, for upscale hair dressing etc).
Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents
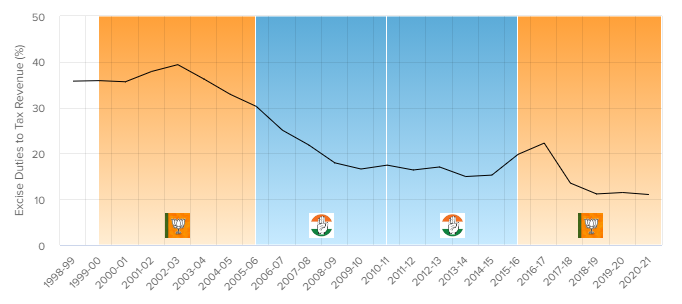
EXCISE TREND
This the contribution to government funds that comes from taxes on manufacturing.
Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents
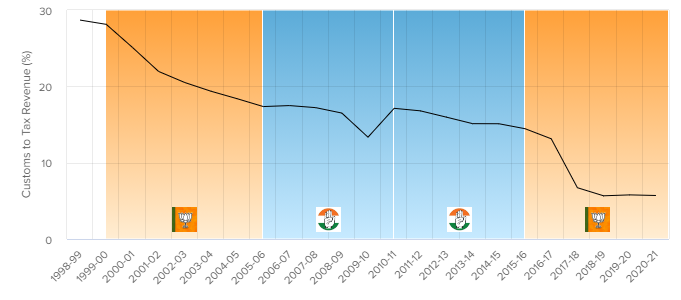
CUSTOMS TREND
Revenues from import duties are the only major indirect tax that the Government of India still controls after the introduction of GST in July 2017.
Data source for this chart: Government of India budget documents